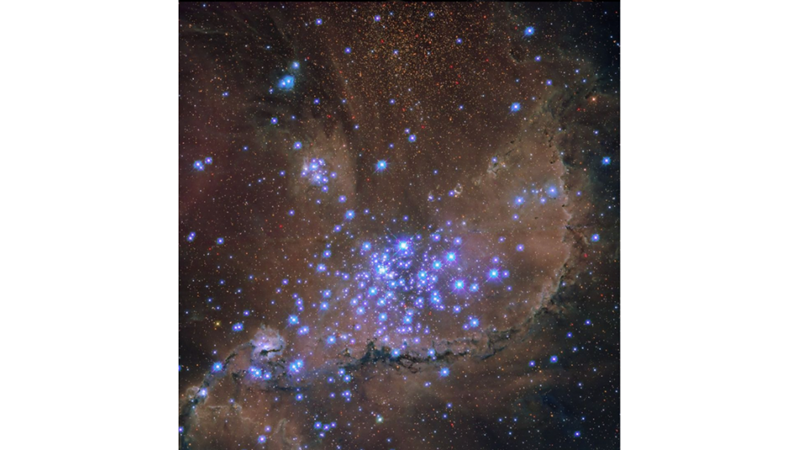
NGC 346
210,000 light years
Small Magellanic Cloud
Located in the Small Magellanic Cloud, one of the Milky Way's closest galactic neighbours, the star cluster NGC 346 is home to hot stars that release radiation and energetic jets. This erodes the denser parts of the gas and dust in the surrounding nebula N66.
Dozens of hot, high-mass stars shine in NGC 346. They may look a little unusual in this new image because Hubble captured them with its unique ability to observe in ultraviolet light.
Ultraviolet light helps astronomers understand more about star formation and evolution. These special observations were collected to learn more about how star formation in a low-metallicity galaxy like the SMC shapes the interstellar medium, which is gas scattered in seemingly empty space.
Astronomers call elements heavier than hydrogen and helium ‘metals’, and the SMC contains fewer metals compared to most regions of the Milky Way. This makes the SMC an excellent example of a galaxy similar to those that existed in the early Universe, when very few heavy elements came together.
Image description:
A group of large, bright, purplish stars dominates the centre of the image. Surrounding them are dark ridges of gas and dust, while in the background more stars crowd the image.
Image credits:
NASA, ESA and C. Murray (Space Telescope Science Institute); Image Processing: Gladys Kober (NASA/Catholic University of America)


 Nielawore
Nielawore








Yorumlar
lovely
Yorum yazmak için lütfen giriş yapınız