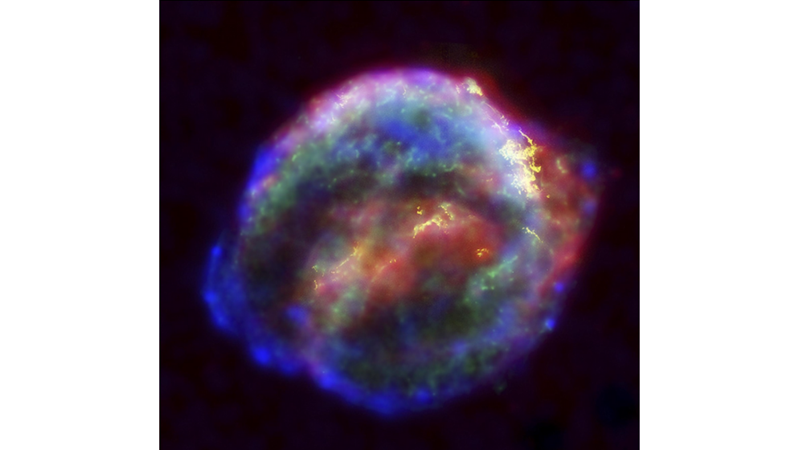
In October 1604, astronomers studying the sky noticed a bright new point of light among the stars. This supernova became known by the name of Johannes Kepler, the German astronomer who studied it in detail. Today, our telescopes continue to observe the slowly expanding remnants of the supernova!
Kepler's supernova remnant, also known as Supernova 1604, looks like a colorful cloud of smoke. The X-rays seen by Chandra are green and blue swirls, mostly at the edges of the remnant, showing regions with millions of degrees of gas or extremely high-energy particles. The yellow optical data from Hubble reveals 10,000 degrees Celsius of gas extending from the center to the upper right of the cloud, where the supernova shock wave struck the densest regions of the surrounding gas. Spitzer's infrared data, on the other hand, highlights microscopic dust particles swept and heated by the supernova shock wave, mostly in the center and along the upper edge, shown in red.
Image description:
Data from NASA Hubble, our retired Spitzer Space Telescope and NASA Chandra Xray combine to search for the expanding remnants of a supernova seen from Earth 400 years ago.
Credits: NASA/ESA/JHU/R. Sankrit & W. Blair


 Nielawore
Nielawore







Yorum yazmak için lütfen giriş yapınız