Recent research suggests that black holes can create their own food supply. Data from the Nasa Chandraxray Observatory and the Very Large Telescope (VLT) show that explosions emitted from black holes can help them feed themselves by cooling the surrounding gas.
The largest galaxies in the Universe are home to massive black holes with masses ranging from millions to tens of billions of solar masses. The jets from these giant black holes continue to grow by consuming the gas around them.
New research reveals that energetic explosions emitted from black holes cause hot gas to cool and form narrow filaments of gas. Some of the cooled gas flows towards the center of galaxies, feeding the black holes and triggering a new explosion. In this way, black holes create a self-feeding cycle, constantly drawing in new gas - a cosmic smorgasbord!
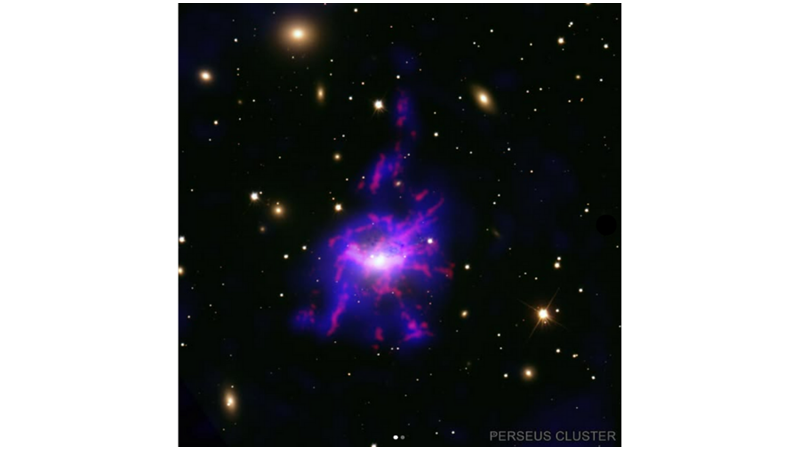
Image description: Patches and filaments of gas, each surrounding a central black hole as it passes through different clusters of galaxies. In each image, a purple patch with neon pink veins floats in the darkness of space, surrounded by particles of light. At the center of each patch is a glowing, bright white dot. The bright white dots represent black holes. The purple spots represent hot X-ray gas and the neon pink veins represent hot gas filaments.
In the Perseus Cluster image on the left, the surrounding light spots are larger and brighter, making it easier to distinguish the individual galaxies they represent. The violet gas has a blue tint, and the hot pink filaments appear solid, as if rendered with the flickering strokes of a paintbrush. The Erboga Cluster is on the right; in this image, the purple gas has a softer, more diffuse quality. The filaments are more detailed, with feathery edges and colors ranging from pale pink to neon red.
Credit: (X-ray:) ASA/CXC/SAO/V. Olivares et al; Optics/IR: DSS; H-alpha: CFHT/SITELLE; Centaurus Cluster: (X-ray:) ASA/CXC/SAO/V. Olivaresi et al.; (Optical/IR:) ASA/ESA/STScI; H-alpha: ESO/VLT/MUSE; Image Processing: NASA/CXC/SAO/N. Wolk


 Nielawore
Nielawore









Yorumlar
really nice
Yorum yazmak için lütfen giriş yapınız