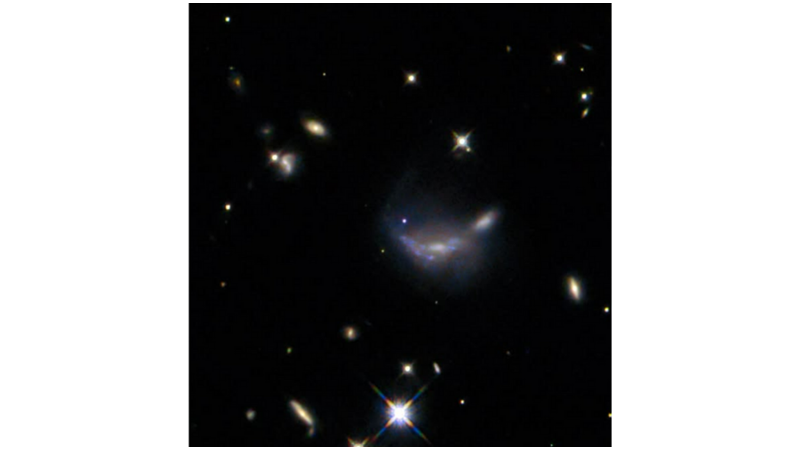
Notice the faint blue dot in the center of the image?
It's actually a supernova explosion observed by Hubble in a galaxy about 600 million light-years away.
This #HubbleFriday frame shows this impressive supernova illuminating the foggy structure of the galaxy.
Hubble made these observations to further study Type Ia supernovae, which occur when the core of a dying star explodes.
Because these types of supernovae have a constant intrinsic brightness, astronomers use them as reliable cosmic beacons to measure distances across the universe.
Scientists plan to observe 100 different Type Ia supernovae with Hubble at different wavelengths, ranging from the ultraviolet to the near infrared.
Image description:
A supernova can be seen as a small but bright blue dot in the center. It is located on the outer disk of a hazy-looking galaxy with a slightly distorted shape. Around it are a number of smaller galaxies that can be seen as glowing disks, and some points of light that are stars close to us on a black background. A few bright stars have X-shaped spikes, which are optical artifacts from the telescope.
Image credits: ESA/Hubble & NASA, R. J. Foley (UC Santa Cruz)


 Nielawore
Nielawore








Yorum yazmak için lütfen giriş yapınız